ACE Inhibitors (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors) are drugs used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure.
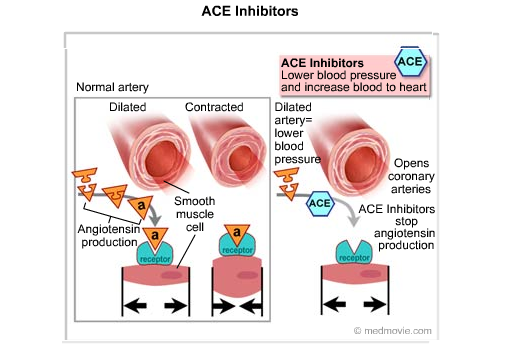
They stop the body’s ability to produce angiotensin II, a natural substance that causes blood vessels to tighten (contract). ACE inhibitors relax and expand (dilate) blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily. This increases the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart, making the heart work more easily and efficiently. (Also known as antihypertensive drugs.
Side effects of ACE inhibitors?
ACE inhibitors are well-tolerated by most individuals. Nevertheless, they are not free of side effects, and some patients should not use ACE inhibitors.
- Skin rash
- Loss of taste
- Chronic dry, hacking cough
- In rare instances, kidney damage
- Women who are taking ACE inhibitors or ARBs for high blood pressure should not become pregnant while on this class of drugs. If you’re taking an ACE inhibitor or an ARB and think you might be pregnant, see your doctor immediately. These drugs have been shown to be dangerous to both mother and baby during pregnancy. They can cause low blood pressure, severe kidney failure, excess potassium and even death of the newborn.
ACE inhibitors that are available in the United States:
- benazepril (Lotensin),
- captopril (Capoten),
- enalapril (Vasotec),
- fosinopril (Monopril),
- lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril)
- moexipril (Univasc)
- perindopril(Aceon)
- quinapril (Accupril)
- ramipril (Altace)
- trandolapril (Mavik)
(From: http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/Conditions_UCM_001087_SubHomePage.jsp)

Comments 1
Pingback: Obesity and a decreased heart function - Cardiac Health